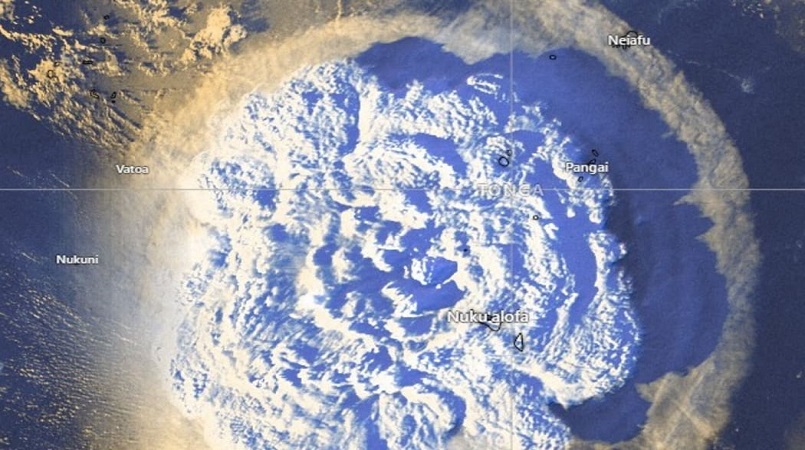
The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai eruption disrupted satellite signals halfway around the world.
An international team of researchers demonstrated an air pressure wave triggered by volcanic eruptions could produce an "equatorial plasma bubble".
An equatorial plasma bubble, or EPB, is a hole formed in the equatorial areas of the ionosphere, which severely disrupts satellite-based communications.
It can delay radio waves as well as degrade the performance of GPS.
An assistant professor at Japan's Nagoya University, who led the research team, says this study will contribute to the prevention of satellite broadcasting and communication failures associated with ionospheric disturbances caused by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other events.
The findings were published in the journal Scientific Reports.
